Simulation and Modeling (CSCI 3010U)
Faculty of Science, Ontario Tech University
http://vclab.science.ontariotechu.ca
Discuss in class
\(\pi\) has fascinated mathematicians since the ancient times. Pick any sufficiently advanced ancient civilization and you will find a mention of \(\pi\). Knowing the value of \(\pi\) is useful in many domains, most notably among them is astronomy. That is why perhaps the ancients were so fascinated with its value. In this assignment you are asked to calculate the value of \(\pi\) using Monte Carlo integration.
Monte Carlo integration is a technique for computing the value of a multidimensional definite integral \[ I = \int_\Omega f(\mathbf{x}) d\mathbf{x}, \] where \(\Omega\), as subset of \(\mathbb{R}^m\), has volume \[ V \int_\Omega d \mathbf{x}. \] In naive Monte Carlo approach, points \[ \mathbf{x}_1, \mathbf{x}_2, \cdots, \mathbf{x}_n \in \Omega \] are sampled uniformly on \(\Omega\). Then, \(I\) can be approximated by \[ I \approx V \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^N f(\mathbf{x}_i) = V \langle f \rangle \]
random sampling. Random sampling is used in many places where exact analytical solutions are too difficult to compute. This is just one instance of such a scenario.
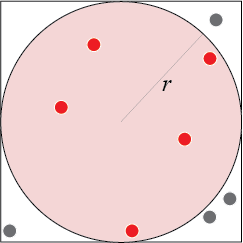
Use the following fact to cast the “problem of calculating \(\pi\)” as a monte carlo simulation:
Area of a circle is \(\pi r^2\), where \(r\) is the radius of the circle.

Complete the following method that computes the value of \(\pi\) through sampling:
def estimate_pi(n_samples, rnd_seed=0):
'''Returns estimated value of pi'''
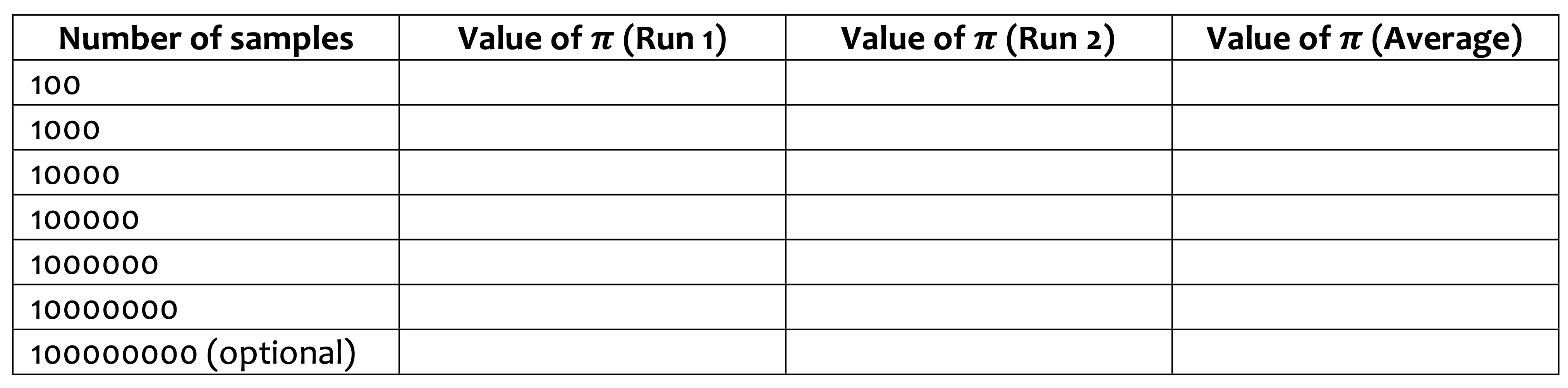
return 0And use this method to complete the following table.
Briefly describe a scheme to check if the value of \(\pi\) that your program has estimated is
any good? Assume that you do not have access to the true value of \(\pi\) (i.e., math.pi). Can you
modify the above program to also return some measure of
confidence in the correctness of the estimated value of \(\pi\)?
Via course Canvas.